Sergio Arcuri
This website contains no AI-generated text or images.
All writing and photography are original works by Ted Vance.
Short Summary
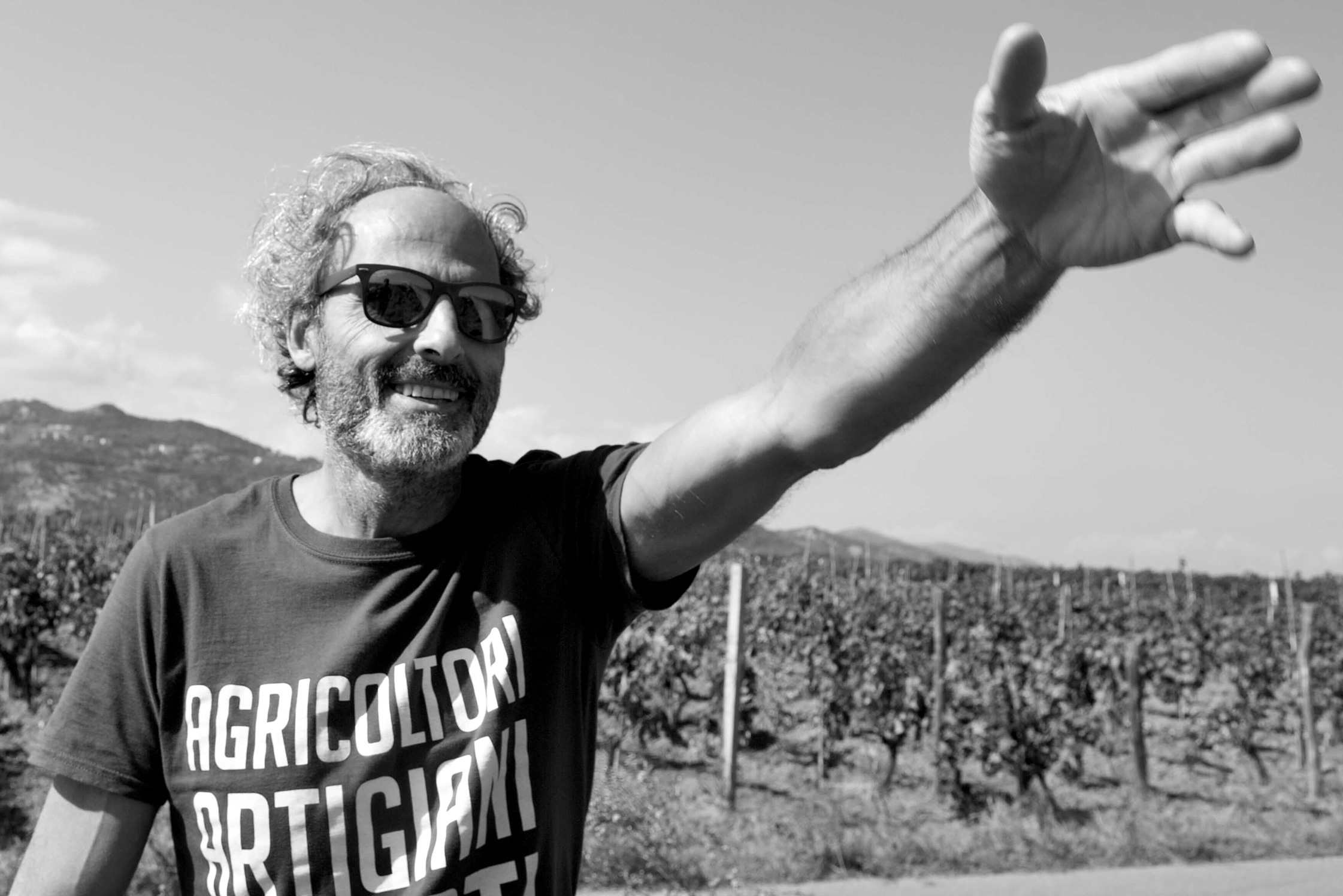
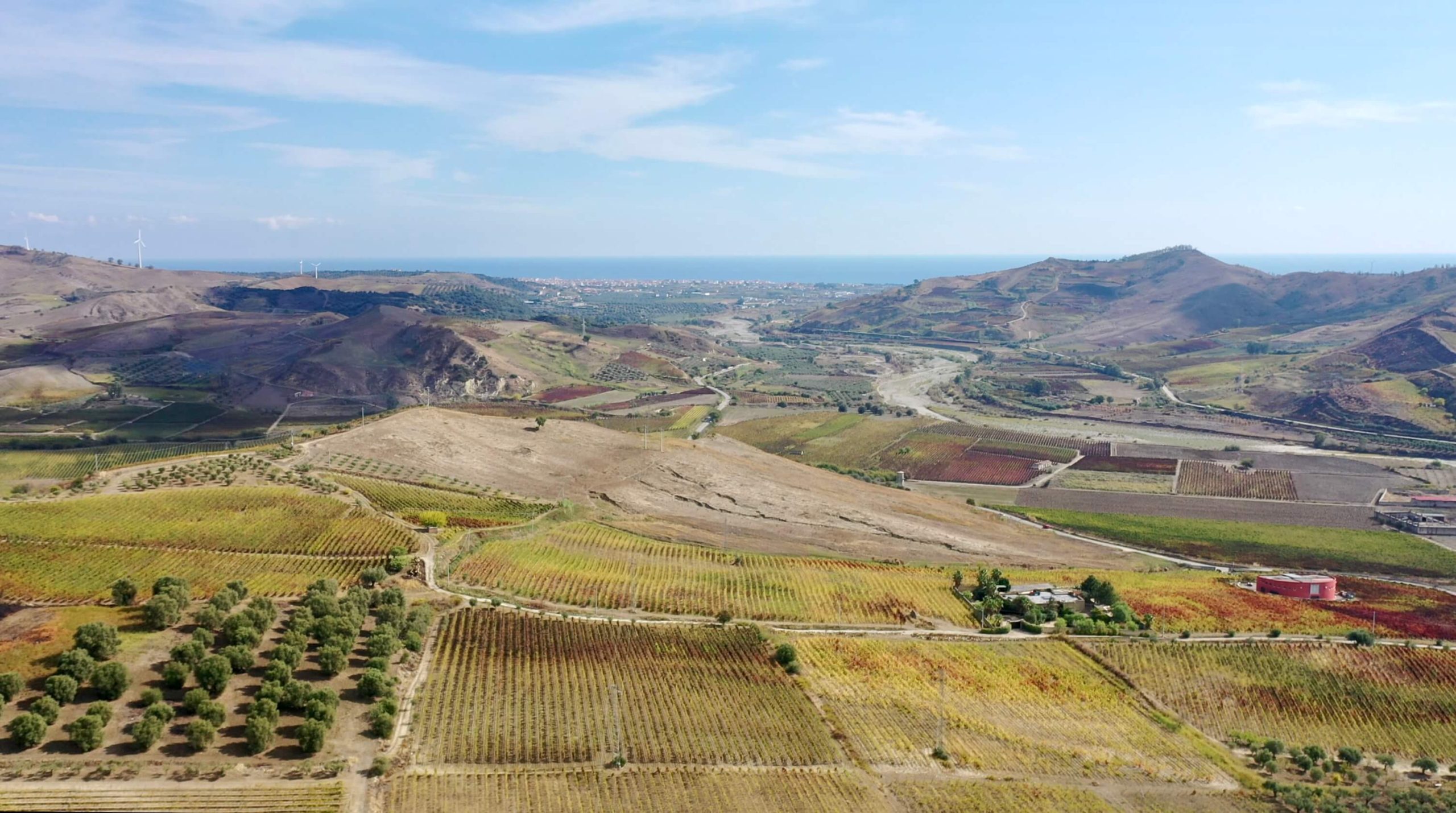
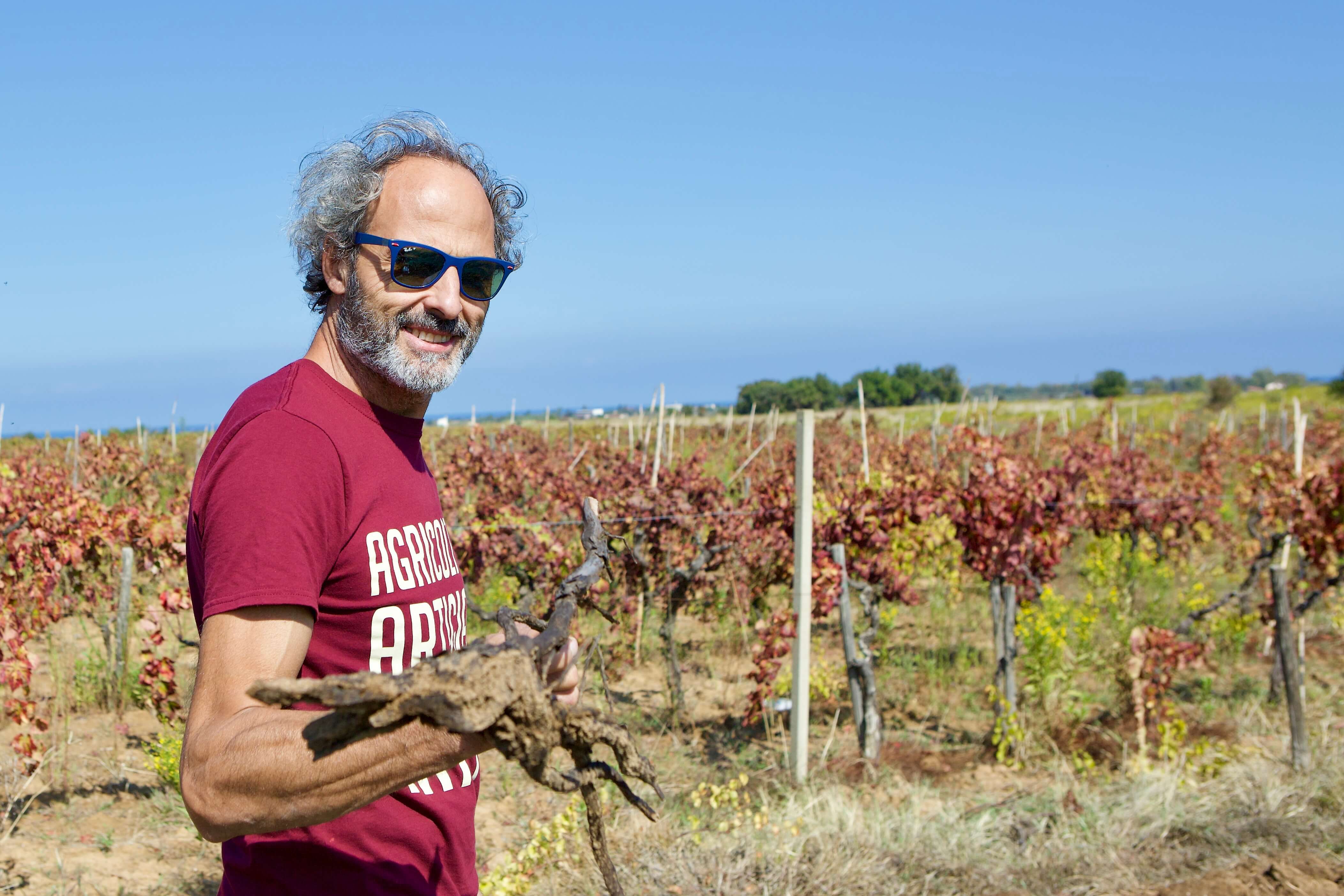
Fourth-generation organic certified winegrower, Sergio Arcuri grew up making traditional Cirò with his father, “Since he was three.” Most of the Ciró’s vineyards extend from only meters of altitude with few beyond 300-400m. The S/SE/W areas from of the hilltop village, Cirò, and on a flat beachfront areas around Cirò Marina are high in calcareous materials. All Arcuri’s six hectares are inside this extremely arid Classico zone with cooling Maritime winds with his highest plots reaching 70m in altitude.Full Length Story
With two glasses cleared of all but the remains of the Gaglioppo primers and a freshly poured two ounces, ten mesmerizing minutes passed as I sniffed and pondered the meaning of wine before the spell broke and I finally took a taste. “But can the taste compete with this nose?” I thought. The aromas were so enticing that I didn’t want to risk downgrading the experience, because they had set such high expectations.
Once I tasted them, both revealed polish and subtlety, depth and affability akin to the world’s most beguiling wines. Perfectly imperfect, Sergio Arcuri’s bottled art effortlessly flowed with intention and artistic signature tailored to the strengths of Galioppo’s individuality, highlighting its terroir with clarity: wafts of iron, blood, salt, and earth; boundless hills of dry grasses, sunbaked and pungent resinous plants and flowers, parched orange blossoms and dried peels, Persian mulberry and microscopic, sweltering wild strawberries, salty sea breezes dancing with hot, dry winds. Pale and rust-tinged garnet reds, Aris, the younger, is darker, punchier, coarser, and the Più Vite is the elder: wiser, more nuanced, and refined. Both express the Gaglioppo’s mercurial nose and deep interior well, with naturally forceful tannins that quickly melt away in the glass.


One of History’s Greats
It rolls playfully off the tongue: Gall-ye-ohhp-po—long A, quick ye-ohhp, hesitation mid-P, and a little pop before the O.
Though relatively unknown, Gaglioppo seems to this taster to be a serious contender for one of the future great red wines of Italy, and Sergio Arcuri is already making noticeable waves —at least to those who know his wines. Through the wines of Sergio and other Cirò revolutionaries, like Francesco Maria de Franco, from A Vita, Gaglioppo adds a Calabrian link to the chain of Italian super-grapes that start in the north with Nebbiolo and drop into central Italy’s Sangiovese and Aglianico regions, just before crossing the Messina Strait into Sicily with Nerello Mascalese, one must pass close through Calabria’s Gaglioppo country.
It may be a surprise to drop this relatively obscure grape into the hat with these vinous juggernauts, but the potential for sublime balance of finesse and power is there—even if fewer examples exist than with other super-varietals. Some grapes in certain terroirs simply have what it takes, and Gaglioppo is definitely one of them. If the past has anything to contribute to this perspective, the future looks good for Cirò’s Gaglioppo as it was once highly respected and one of Italy’s most important wines all the way back to the Romans, as was the neighboring DOC, Melissa. (Imagine what kind of resilience a wine needed to travel from Cirò to Rome two thousand years ago!) Despite being nearly forgotten, Galioppo has always been and will remain one of the longest-standing, unshakable pillars of Italian red wine—the last great gladiator in the coliseum. In the face of climate change, its ability to thrive in the dry and hot conditions in Cirò is the vote for longevity of this ancient style. It appears that conditions haven’t and won’t change as much as in other top-quality regions, and Sergio says that the alcohol levels today are more or less what they were decades ago.
While it’s hard for the most celebrated historical continental climate wines to maintain lower alcohols and the freshness of the past (areas like Wachau, Langhe, Burgundy, Rioja) Sergio says that Gaglioppo hasn’t changed much over the years except that budbreak can come a little earlier, and he even insists this is not definitive. And of course, it’s not at all a continental climate; some of Sergio’s vines are ten steps from the beach. Extremely susceptible to mildew pressure because of its thin skins, Gaglippo’s ideal home for millennia has been on this arid Ionian seaside stretch of hills and beachfront property.
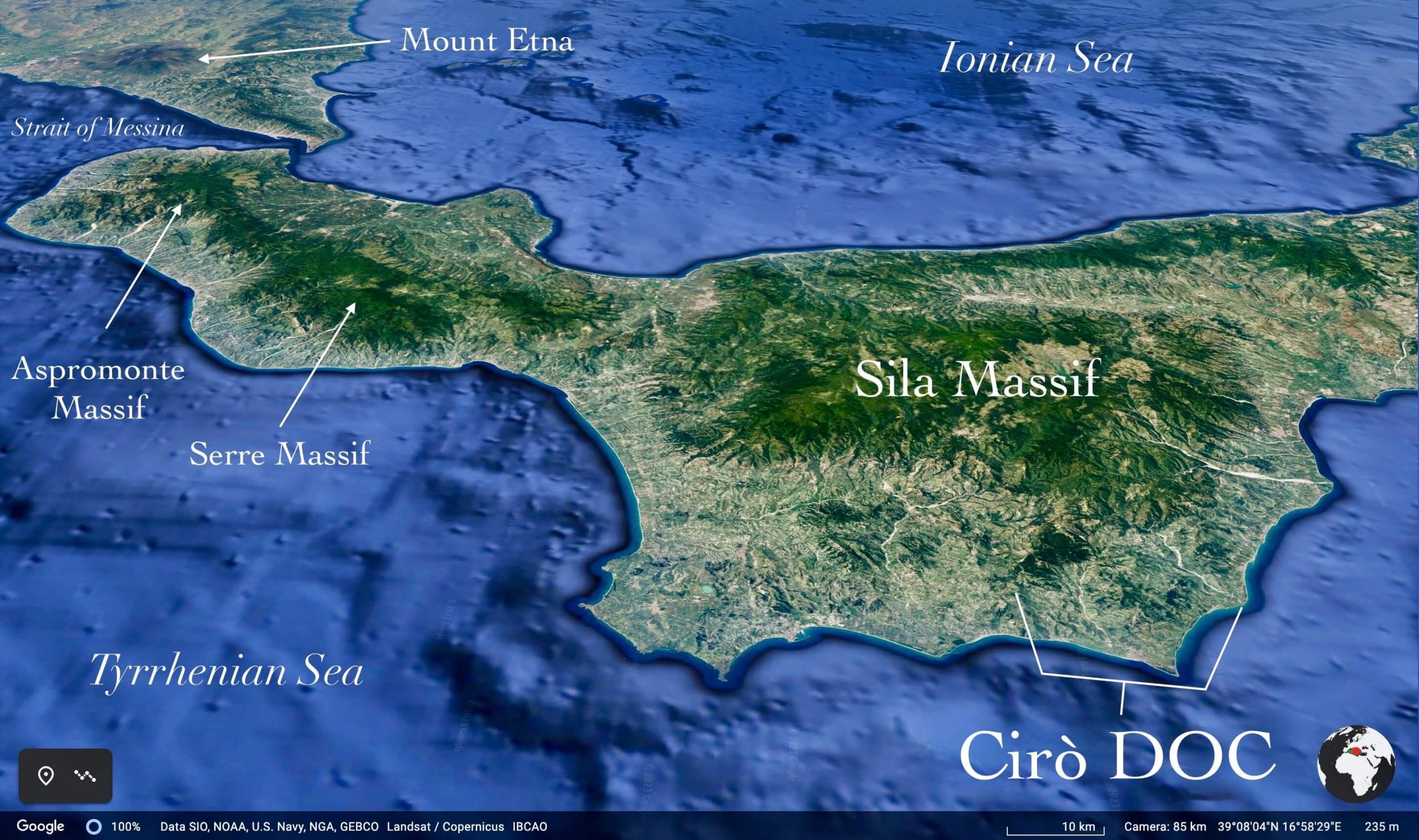
Because of the Sirocco winds that cross the Mediterranean from the Sahara and the northern Tramontane winds that pass through the dry Basilicata directly north, combined with the Sila Massif to the west, there are years where no treatments for mildew are needed. Having no foreign inputs into the vineyards at all is as natural as farming gets! When there is the rare high mildew pressure year, Sergio says they apply one or two treatments maximum, and only in specific plots, not the entirety of his vineyards. He explains that those not practicing quality farming, even the worst of them, spray only as much as six times in a season—lower than most famous wine regions, and half that of what many organic vineyards in other regions require.
Gaglioppo’s potential for greatness lies in its genetic material and its perfect situation in Cirò. There are many different claims to its genetic relations, which include Sangiovese, Aglianico, Nerello Mascalese and Frapatto as offspring or parent—three of the four named superstar Italian grapes. Yet it has the most in common with Nebbiolo: naturally paler color, fresh acidity, big tannins (if they’re not tamed), and incredible durability that could match history’s superstar wines. So, what’s holding it back from the big game? Perhaps the first hurdle could be Calabria itself.

The Shackles of Calabria
Calabria is the poorest department among Italy’s twenty. It was last place in GDP per capita as of 2017, and not much has likely changed. But one might say that parts of Piemonte, including the Langhe, were also at rock bottom before Barolo and Barbaresco led the entire region to world celebrity and immense wealth. Could Cirò do the same? The financial incentive to make great wine in Calabria is low, and the consumers of these wines, crafted with quality over quantity, are not local—they aren’t even in Italy. They’re in Northern Europe, or overseas in markets such as that of the US. Calabria is also at the end of the Italian peninsula, so no one passes through on their way to somewhere else. It was a maritime crossroads centuries ago, but by car it’s a slog, and any European flight not originating from Rome can be a day of travel to one of its small airports. To get to this ancient, chaotic civilization on the southern fringe of Italy, you must want to be there.
Sergio was born in Cirò Marina in July of 1971, two years after the Cirò DOC was created—one of the first in Italy, along with today’s greats, like Barolo and Brunello di Montalcino (the latter two eventually became DOCGs in 1980 with the G upgrade). He grew up making traditional Cirò with his father, “Since he was three,” he says, and from early on he knew he wanted to make wine. “It was always in my head, even when I was busy with other work.” At age 38, after working some years in Sardinia and Milan (though never missing a harvest in Cirò), he came to a point where he knew he had to make the leap back home to follow his calling. He bottled his first vintage in 2009, commercialized his first rosato in 2010 and rosso in 2011. Today he leads the family’s winemaking and vineyard efforts with his brother and nephew.
As we walk out of Sergio’s dimly lit cul-de-sac onto Via Roma (SP5) that’s a straight shot down to the marina before hanging a right to the south, he glides through the chaos like a summer breeze, or like water, at the rapid pace of this central Napoli-esque village. It’s cinematic, almost exaggerated in its setting, with people from central casting in their places. Action! Pedestrians swarm in the dimly lit streets (crosswalk anyone?), cars zip by (if you don’t walk in front to get them to slow down to cross you’ll be on that corner all night!), old Italian guys huddle outside snacking, smoking, drinking, talking. You also feel others watching you but you don’t see them; Calabria, is one of Italy’s most notorious mafia hothouses, so everyone has eyes in the back of their head. As Sergio’s arms and hands gesticulate wildly in the national language of the body, his eyes dart around like a spy keeping watch for a KGB tail.

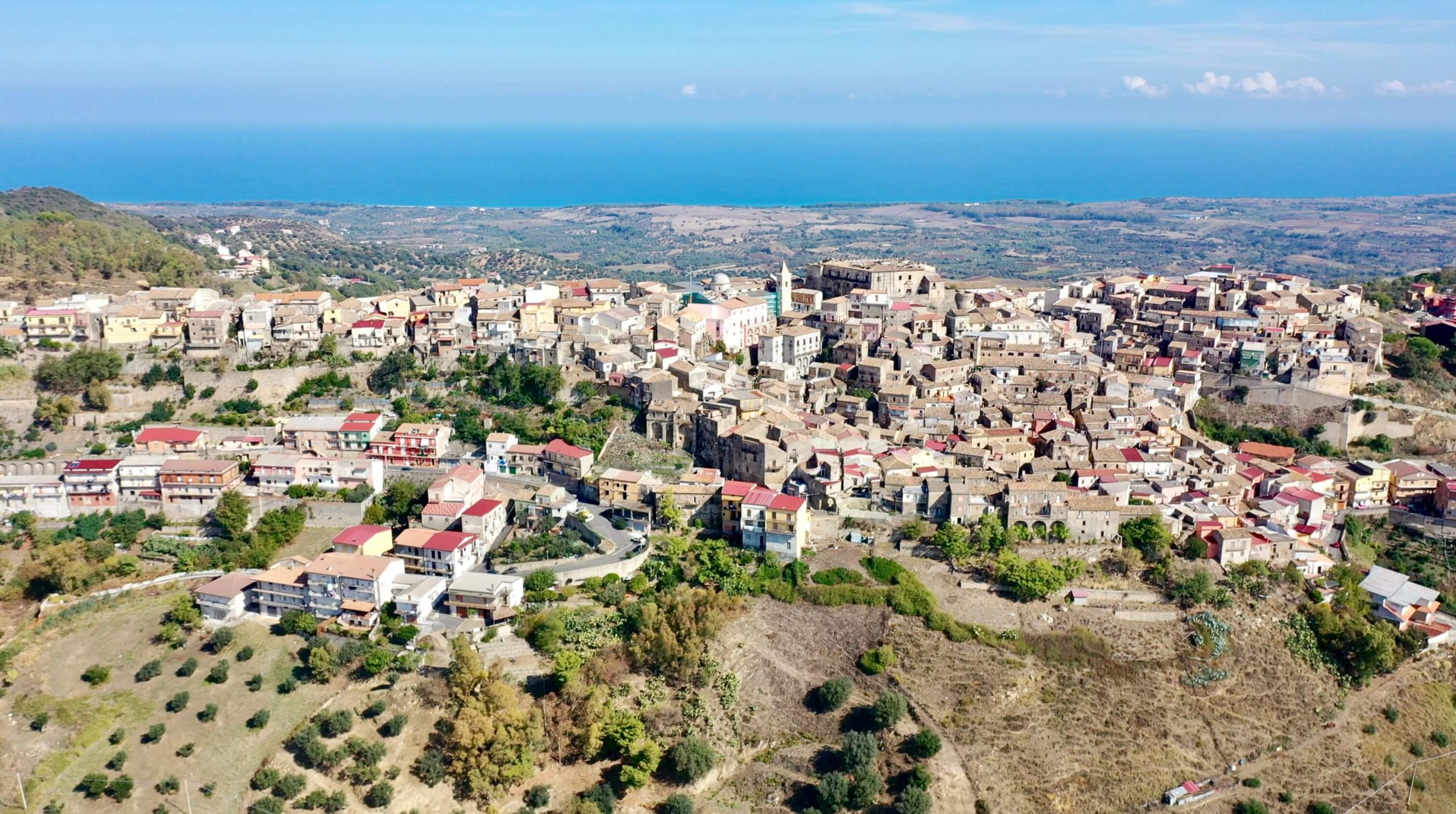
Sergio points to the wall of buildings ahead of us as he crosses the street, his Italian being translated by his friend and our impromptu guide, Marco Salerno, a part time local winemaker living and working in public health full time in New York City—like I said, straight out of the movies. “When I was a kid, those buildings didn’t exist,” Salerno relays from Sergio. “My mother’s house was here, but all this was agricultural fields. Can you imagine that?” Cirò Marina and the surrounding residential areas were slapped together like France’s bombed-out village centers after WWII, creating one of the strangest juxtapositions of beautiful and horrific architecture in such a magical country. Except here in Cirò the buildings weren’t bombed. There was/is little money, and it desperately shows in the dilapidated buildings and ubiquitous tombstone-like, hollowed out concrete buildings half-started decades ago that uglify such gorgeous natural coastal beauty. (Don’t go to Calabria for posh accommodations, unless you know the secret spots only the locals know.) Here, it’s all about the countryside and looking into the dreamy blue and green shades of Tyrrhenian Sea on Calabria’s northside, the Ionian to the south (Cirò country), and the gorgeous ancient mountain landscape, with stretches that seem untouched by mankind, though it has been well trodden by humans since before the world’s first known alphabet.
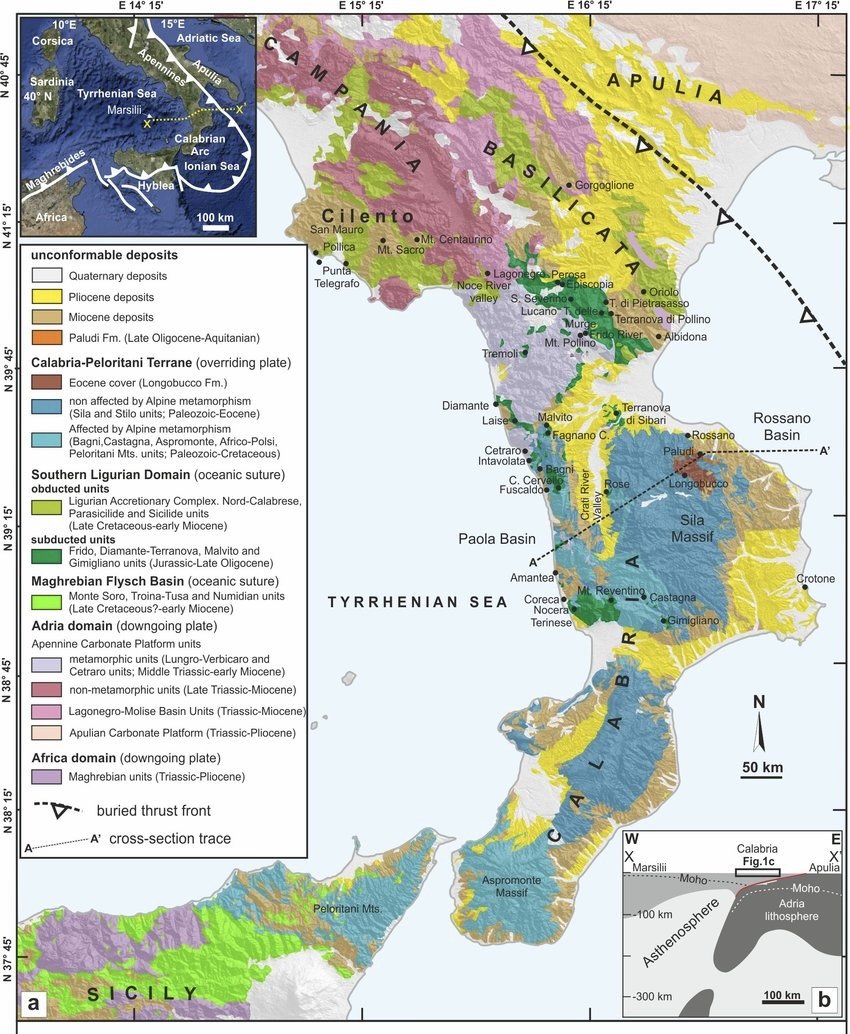
Before Written History
The mountains of Calabria are remnants of Pangea, Earth’s last supercontinent, a time when all of today’s continents were scrunched together. They’re what is referred to as the Variscans, an ancient mountain chain that once connected France’s Massif Central and Massif Armoricain, the Iberian Massif (including the Galician Massif), the Bohemian Massif, two-thirds of Corsica and almost all of Sardinia, and believe it or not, the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern US—formations that predate all the famous limestone wine regions of Western Europe by more than 100-million years. Though this ancient formation is dominant in Calabria, Cirò’s soils have very little to do with it.
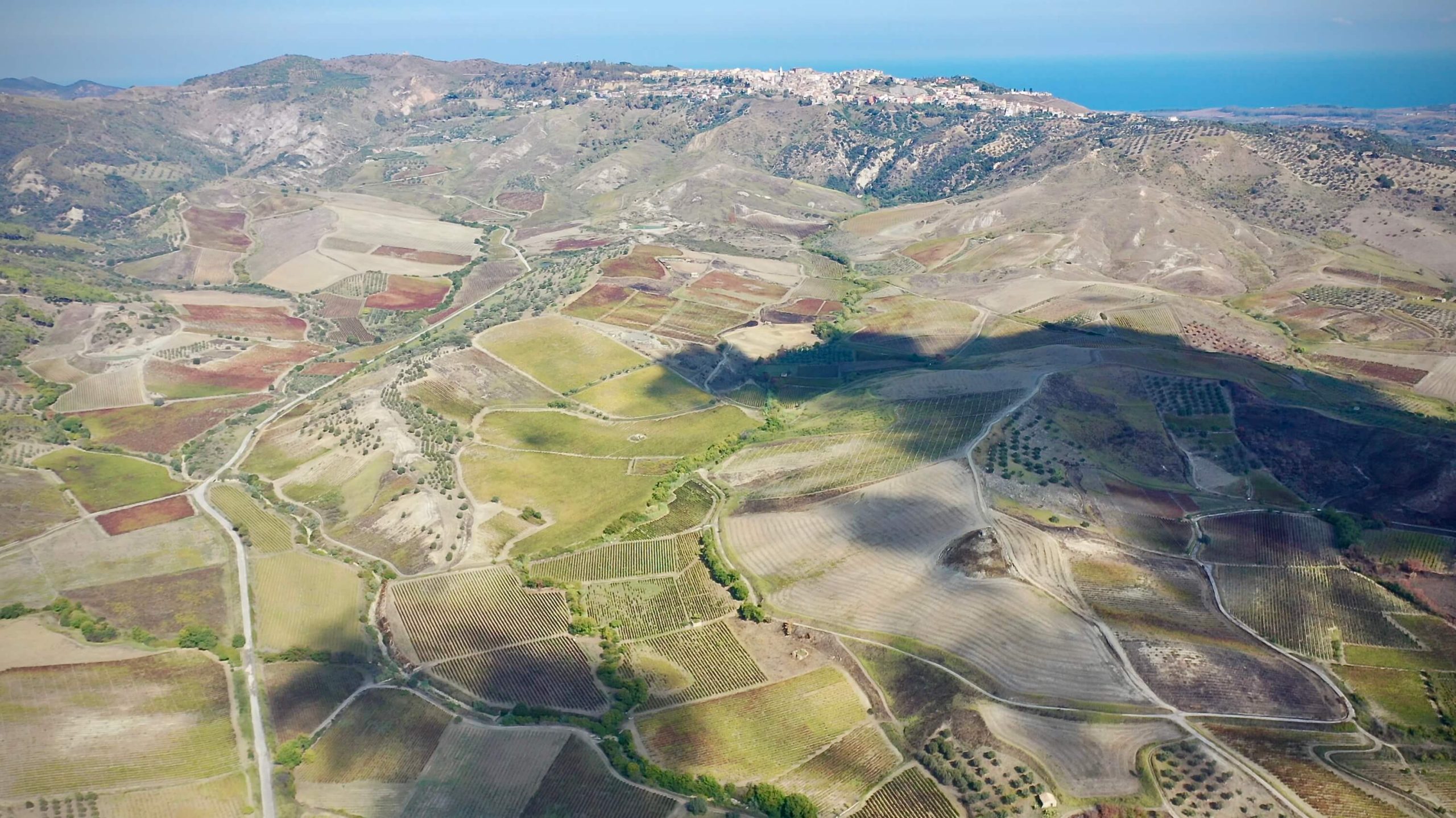
Cirò’s vineyards are in more recent geological deposition from between the Miocene, Pliocene, and Quaternary—23 million years ago to today. They are the same age as many wine regions, such as France’s Southern Rhône Valley (as well as parts of Crozes-Hermitage and Hermitage), Languedoc and Italy’s Langhe–-home to Barolo and Barbaresco, but they’re composed of different materials. Despite Cirò curious similarities to Nebbiolo (especially those with longer cellar aging before bottling), the depositions that make up the better soils are different, and so is the overall terroir of the Cirò DOC. Most of the vineyards of the region extend from only meters above the sea and few reach beyond three hundred to four. There are areas with higher quantities of calcareous materials than others (like Langhe), with the majority either south, southeast and west of the hilltop village, Cirò, and on a flat area above the beachfront of Cirò Marina. On the northside of Cirò, there are less calcareous materials between the two townships and the areas toward their north side—note on Google Earth (see image) where the soil is whiter toward the south (on the left side of the image) and the darker soil in the north (on the right side)—it’s as clear as brown and white!
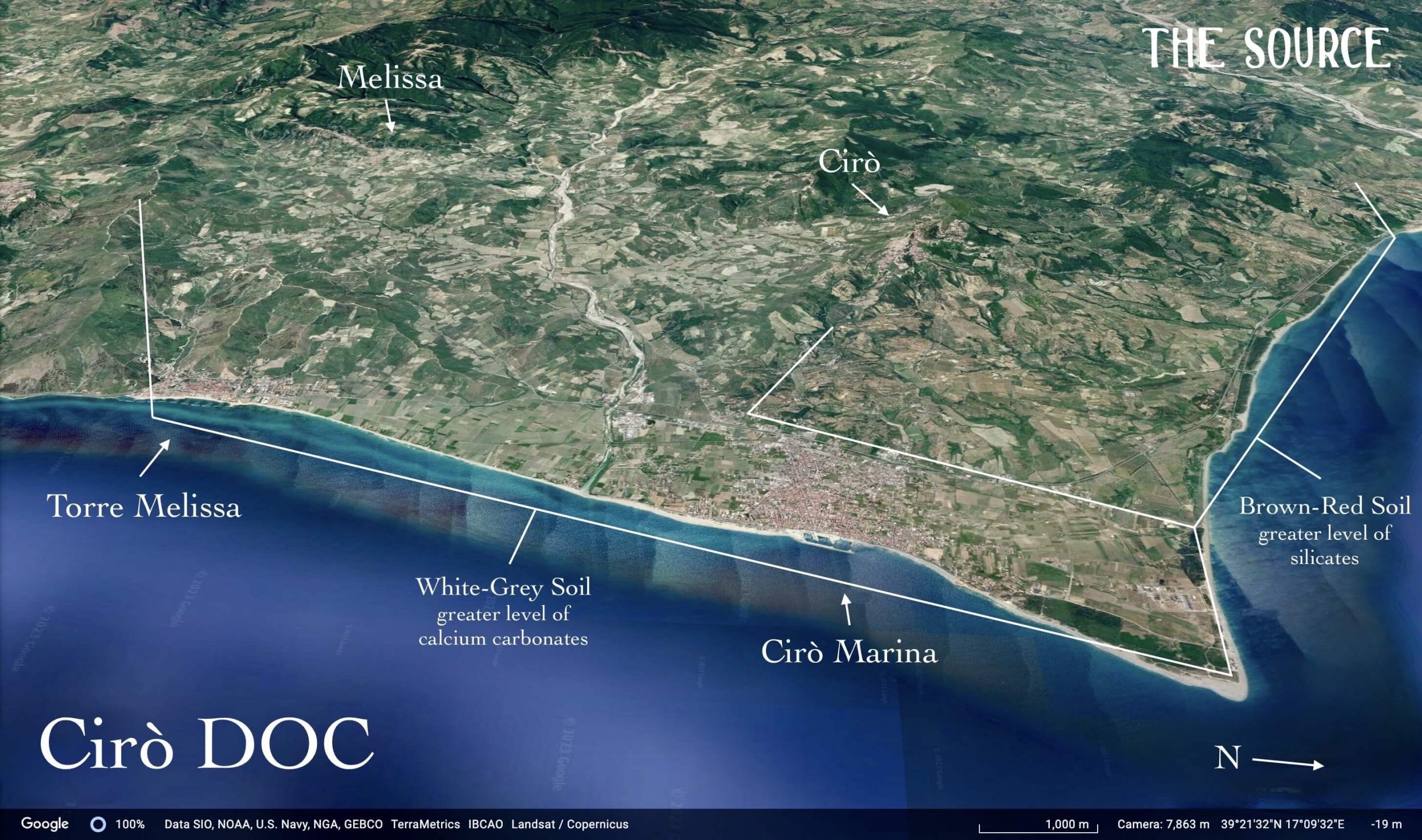
The Story of Cirò, According to Sergio
“The history of Cirò is very long, and viticulture in Calabria is thousands of years old. It’s not known precisely since when grapes and wine were produced, but certainly when grapes were first produced in Calabria, the rest of Italy had nothing. In fact, Calabria was named Enotria, “land of wine.”
Though the Cirò DOC was born in 1969, other viticultural areas of Calabria were abandoned and many Calabrians emigrated to northern Italy and abroad. In the last decade, the recovery that started from Cirò finally began. I am one of the pioneers along with other winemakers who started bottling the real Cirò, we call the group the Cirò Revolution.
Today Cirò is growing as it was in the past from 1950 to 1990, thanks to the Cirò Revolution. Even the historic cellars, the ones that made the Cirò decline in recent years, have regained their motivation and are growing. There are two visions among the producers, given that the DOC disciplinary allows the addition of 20% other grapes, including international ones, which certainly loses the true characteristics of Cirò. Most of the producers of the Cirò Revolution produce it entirely with Gaglioppo. This was the real revolution that restored vigor and interest in Cirò.
The most important thing that stopped Cirò from becoming famous today like other wine regions who were also not so famous in the recent past, like Alto Piemonte, Montalcino, and even Langhe (which became more famous in the last 30-40 years) is that it does not have a specification suitable for the vine. The specification suitable for Cirò is that of Barolo, and it is often called the Barolo of Calabria: Gaglioppo gives its best after at least four years of refinement, but I prefer after six years. In the 60s and 70s Cirò was produced with a minimum of five and eight years of refinement and it had a high price and an excellent reputation, especially in Piemonte, but also in the US. After that, many cellars at the time (who are still working today) instead of continuing the path of quality, chose the path of quantity. They exploited the name Cirò but inside the bottle there was little or nothing, wines without soul, without identity, wines for large-scale, low-level distribution.
After almost destroying the name Cirò, in the 90s they started producing IGP Calabria wine, highlighting the name of the winery on the label, almost ashamed of the name Cirò. Luckily the winemakers continued to produce quality Gaglioppo, and I can say with certainty that if we at the Cirò Revolution hadn’t started bottling over ten years ago, Cirò would no longer exist today.”

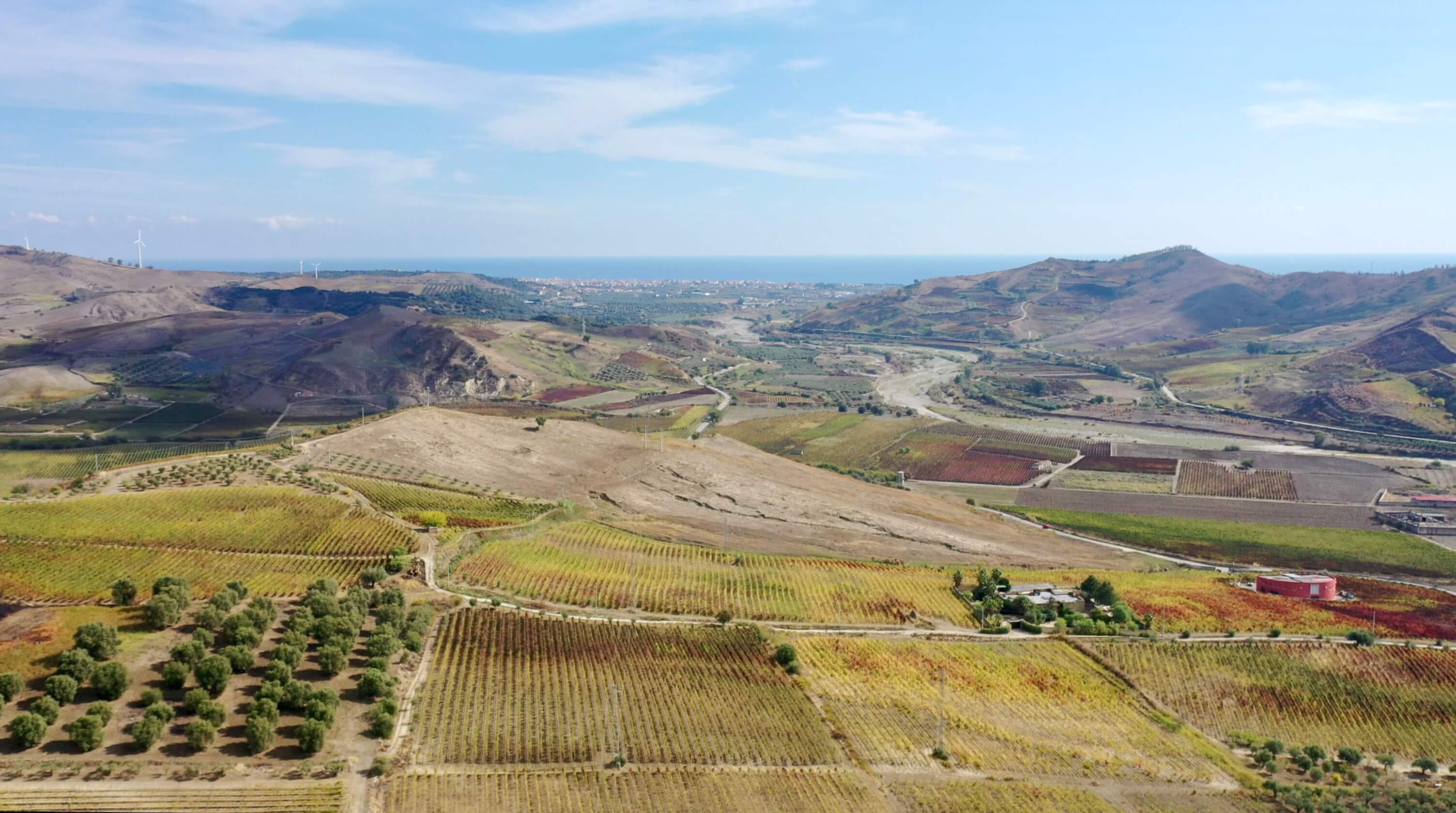
Arcuri Vineyards
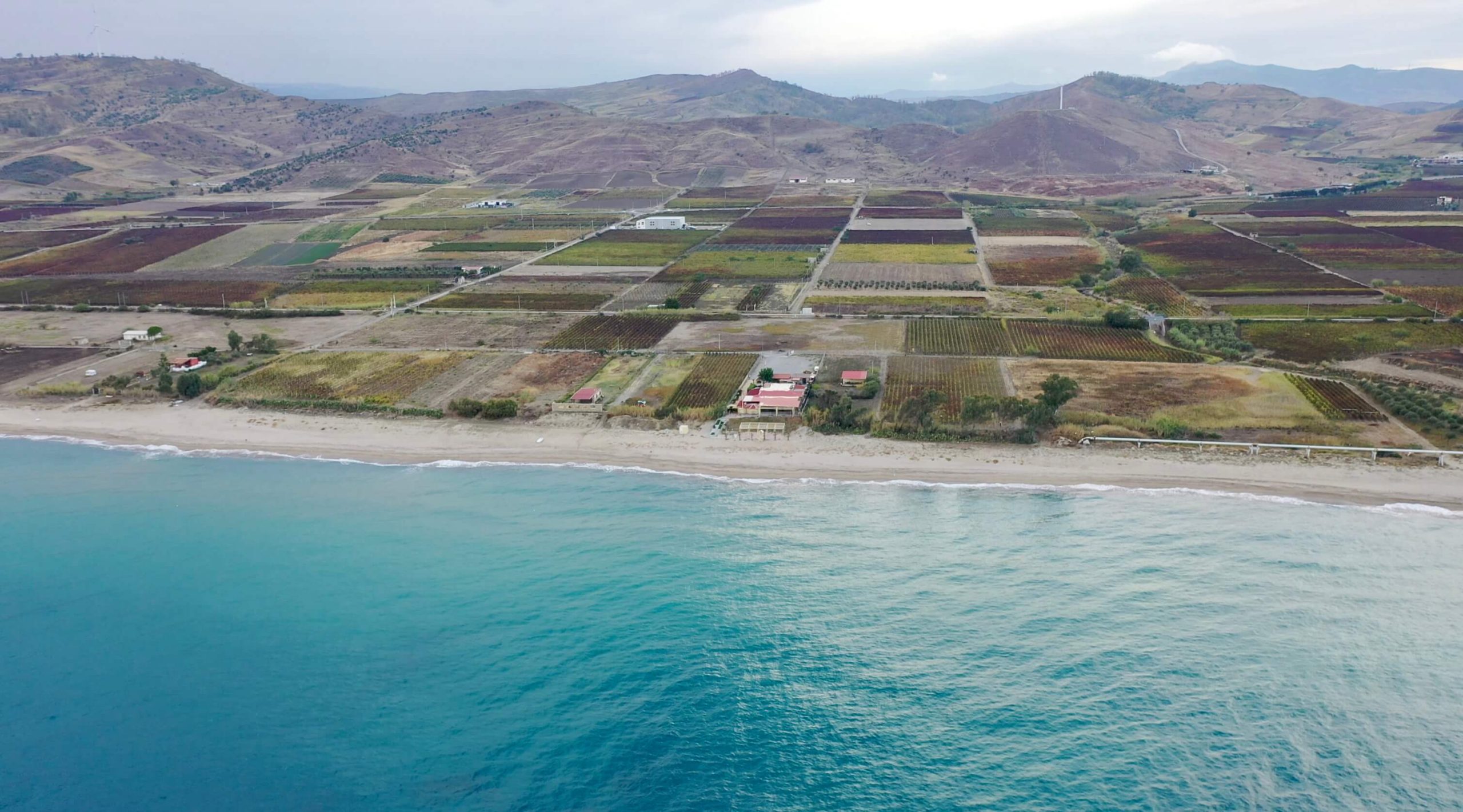
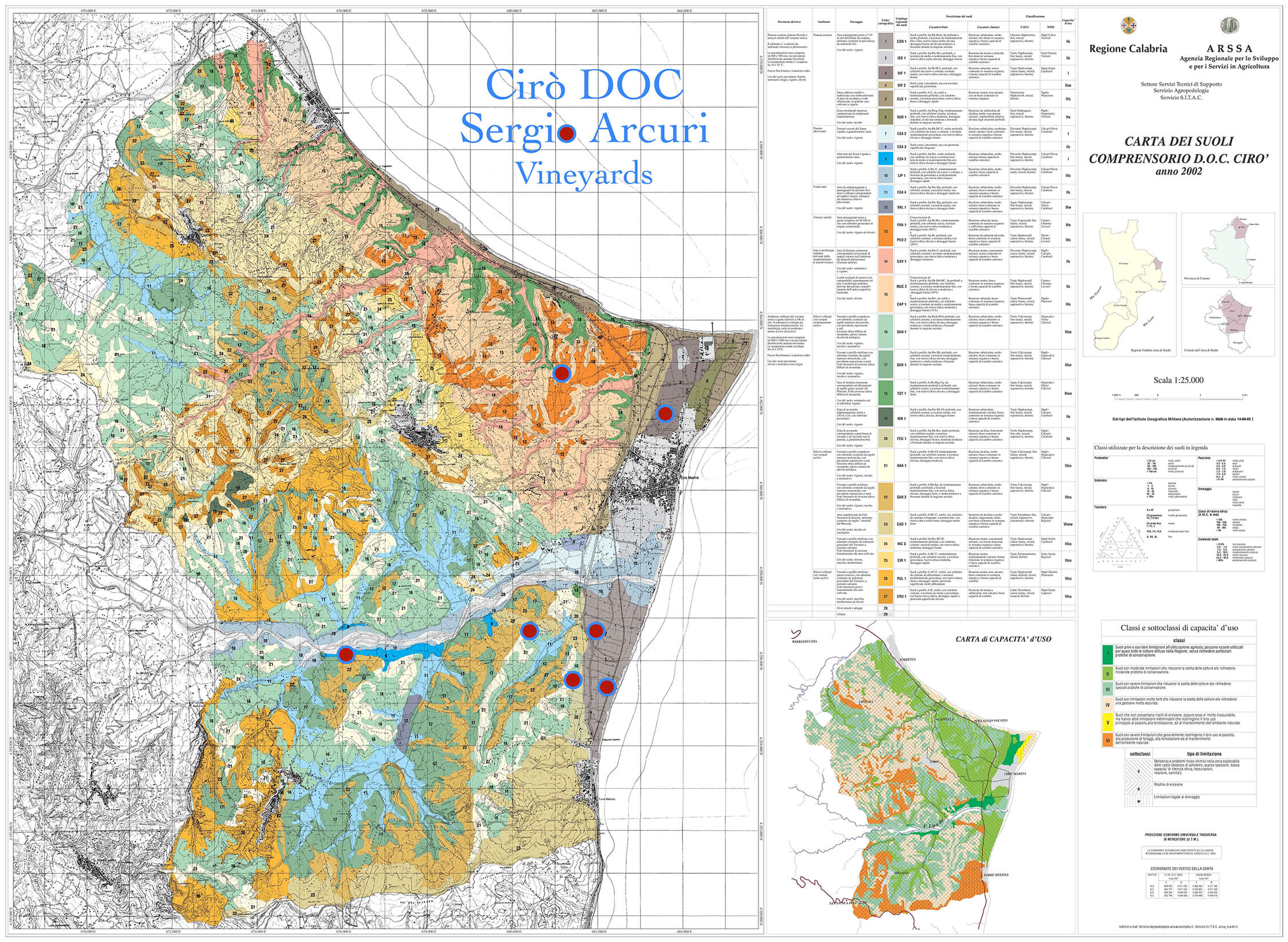
Sergio says that an in-depth study of the region’s terroirs has not been done, even if there is a great diversity of soil and microclimate change from area to area. The DOC was determined by the municipal boundaries of Cirò and Cirò Marina for the classic Cirò DOC, and the neighboring municipalities of Melissa and Crucoli can also make Cirò DOC, though Cirò Classicos (Classico, Classico Superiore, Classico Superiore Riserva) can only come from Cirò and Cirò Marina, which has only 490 hectares. All of Arcuri’s vineyards are inside the Classico zone.
The Arcuris have made wine in Cirò since 1880, and with the knowledge passed down through the generations, they know a few things about Gaglioppo’s interaction with the various terroirs and their output. Sergio explains that the principal ingredient for high quality Gaglioppo is clay, not its visual grandeur. Clay is found throughout the entire appellation, and it’s especially deep in the flatter areas by the sea as a result of the Lipuda River delta. Often contrary to wine books and articles on Cirò, Sergio believes that wines grown on the flatter areas in deeper beds of calcareous clay make Cirò with as much–if not more–quality than those on the picturesque steep, exposed hillsides—similar to Cabernet Franc’s predilection for deeper clay topsoil in Saumur-Champigny. “There’s no need to make wines on the hills. We have the beautiful Ionian!” It’s true that the flashiest vineyards don’t always make the best wines—case in point: Côte d’Or.
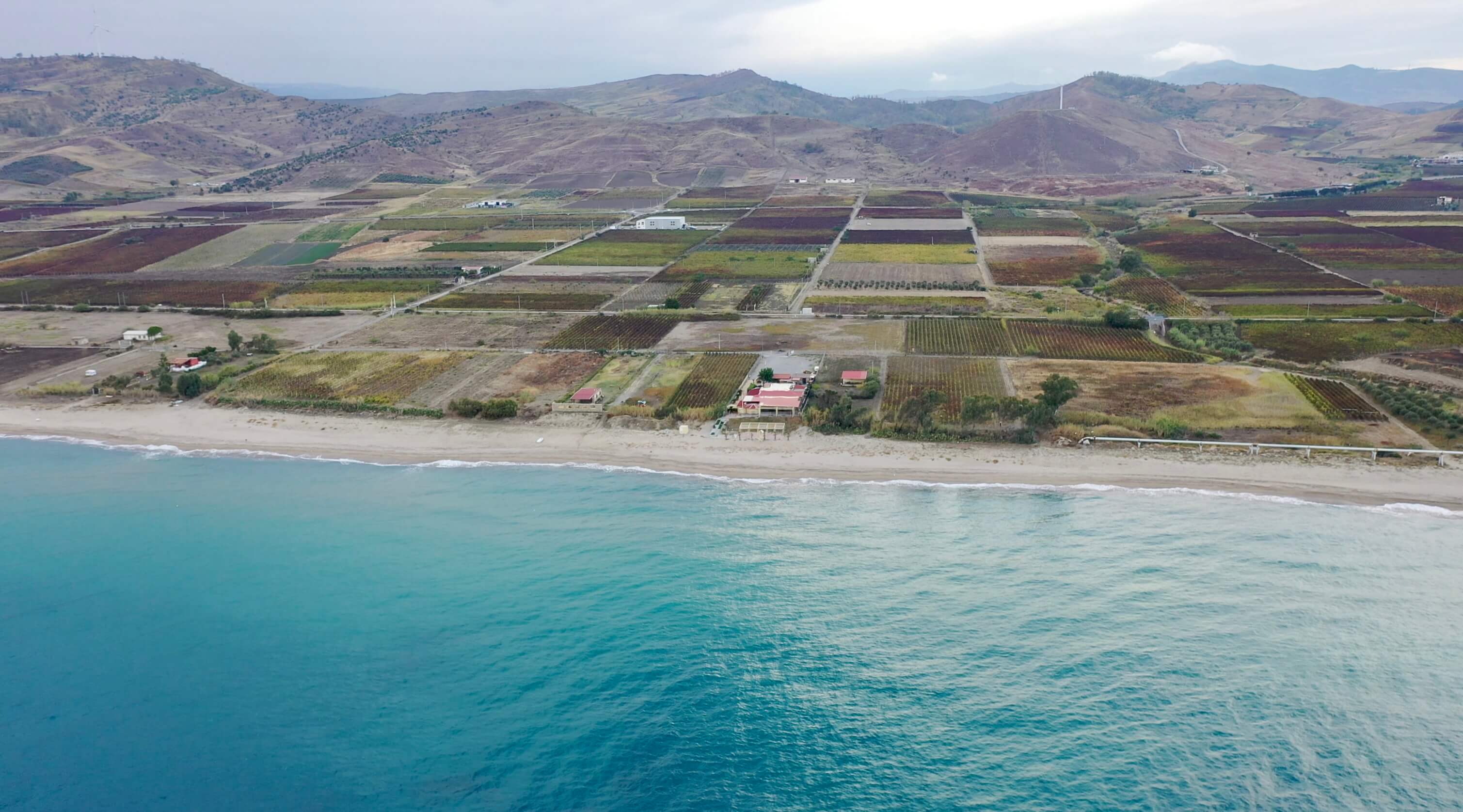

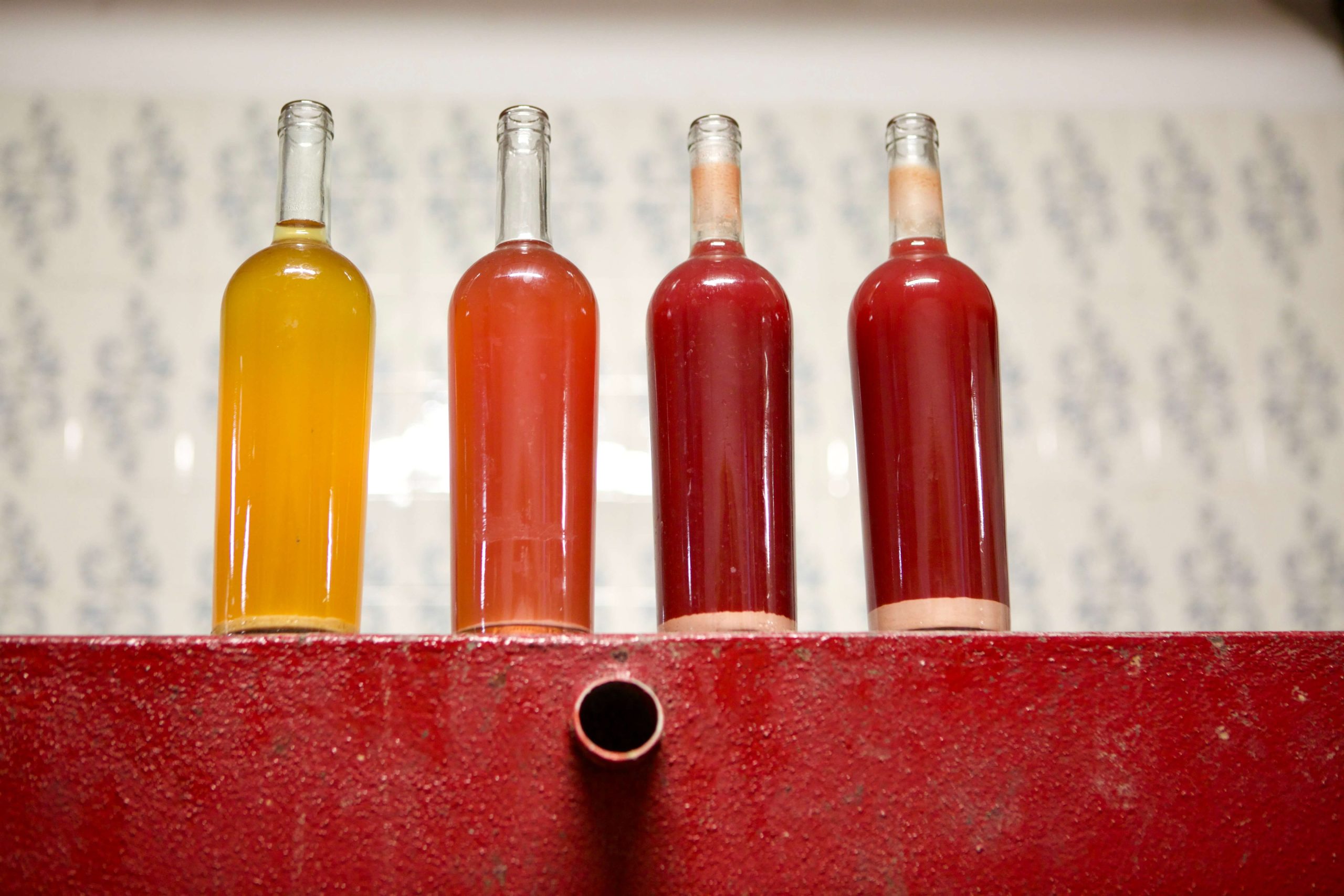
Most of Arcuri’s six hectares of vines are on the plain beside the sea, with the highest reaching 70m in altitude. The average vine age is thirty years old, with the oldest parcels being seventy. Sergio explains that his biotypes of Gaglioppo are not known, but all his replanting is done by massale selections from his vineyards that produce smaller bunches and the highest quality grapes. Each plot is selected based on its terroir and quality for either the rosato, rosso, or the bianco, the latter being made entirely from the indigenous grape, Greco Bianco.
During the fruit ripening period, the diurnal shift in the summer ranges only about 8°C (15°F), which could be expected for this beachfront property, and the mid-fall about 12°C and late fall 15°C. The very active maritime winds in this period help to keep the grapes cool and fresh even when the temperature jumps above 40°C (104°F).
The Arcuri’s have always worked their vineyards in a natural and organic way. In 2010 they began their adherence to the rules for organic certification and have been certified since 2015. Sergio is also interested in biodynamics and believes that he already practices many of the principles but hasn’t yet found how he might approach it when his vineyards already don’t need the addition of unnatural treatments to keep nature’s adversaries away from the vine.


Gagioloppo
Sergio also says that despite Gaglioppo’s brickish red color with orange reflections, it’s very stable against oxidation. It’s also not prone to reductive elements, which makes it versatile with many approaches in the cellar and different styles of wine, including very good rosato. Gaglioppo’s Achilles Heel is its thin skins and the vine’s sensitivity to Peronospora and mildew, which has greatly limited its proliferation. Cirò Marina has an average of 670mm (26 inches) of rain each year, which is decent, but during the late spring and summer when the plants begin to produce chlorophyll—the food for Peronospera and mildew—it’s very dry. Between August and October, even if it rains, it’s too late for these fungi to have a big impact because the hot, dry winds clean out the vines in a heartbeat, and usually the latest picked Gaglioppo comes in at the beginning of October, before the highest amount of rainfall begins to fall. It’s good that there isn’t much rainfall during the growing season because it can have high production, and with clay as the main topsoil (key for water retention during the summer drought) the vines could produce too much for high quality wine.
Gaglioppo’s skins are delicate and thin but have a lot of tannin. Sergio describes the skin tannins as elegant and velvety, and the seeds contain even more. “But you need to know how to manage maceration well and to choose the right vineyards based on the type of wine you intend to produce,” he says. Some vineyards produce grapes most suitable for rosato or a short-fermentation maceration rosso, and those with the greatest balance of skin and seed tannin maturity should be destined for the longer vinification and aging.
“Gaglioppo’s deception with wine professionals, even though it has its own personality, the color, spices, minerality, and structure expressed with long aging, think that it is aged in large barrels when its aged entirely in concrete, or glass. Many fall for it, and I don’t use any wood vats in my cellar.”


Used in the past to lighten up Gaglioppo, this white grape native to southern Italy is very resistant to disease (in addition to Cirò having a relatively disease-free environment) because of its thick skin’s high level of catechins—colorless phenolic compounds that impart tannin and, in this case, a welcome refreshing gentle bitterness classic to great Italian wine. It’s also very resistant to oxidation–also thanks to the catechins, doesn’t have a lot of sugar when fully ripe, and maintains a medium level of acidity. Sergio’s Greco Bianco “Liberaisensi,” which loosely means “blindfolded,” or “tasting blind” is macerated on its skins for two to three hours before pressing and naturally fermenting (max temp of 20°C) and aging in steel prior to a light filtration before bottling. Total SO2 here is 35 mg/L—quite low for a white wine, but more stable at this level because of the skin’s contribution to antioxidation and extremely clean fruit upon picking. Because it doesn’t go through malolactic fermentation, it is filtered before bottling.

The range of three Gaglioppo wines begins with the salmon pink and brick colored, pale Calabria IGP Rosato “Il Marinetto,” which comes entirely from within the Cirò DOC area and is the first fruit of the season to be picked, usually at the beginning of September. Like many rosatos made from serious materials and top tier Italian grapes, like Nebbiolo, Sangiovese and Nerello Mascalese, in body and color it’s somewhere between a classical Provençal rosé and a very light red, and in this case with Gaglioppo, always with an orange tint and fuller color, even with only three to four hours of skin maceration prior to draining off the juice; the press juice is not used because Sergio wants it to remain fine and to reduce tannin extraction from the skins. (The press juice, along with all the other quality materials excluded from each pressing of white and red grapes goes into a wine he sells to local friends.)
Its maximum temperatures usually reach around 20°C but are not temperature controlled. It’s more in the style of a Valle d’Aosta Premetta (Grosjean comes to mind), some of the red and white grape rosé blends out of Portugal, or Spanish Clarete, another hybrid somewhere between red and rosé. It’s serious wine and Sergio insists that even more bottle time is beneficial despite most people wanting to drink it young because that’s what people were led to believe about rosés cleverly marketed by the French for fast turnaround on cash on their investment. Those familiar with French rosés know the best age quite well in the short term and are better with more bottle time than a few months, or even a year.
Il Marinetto emits aromas of Aperol, pink lady apple skin, pink flower, orange marmalade, tamarind, peach pit, flan syrup, partially dried apricot, and sweet licorice. It’s mouthwateringly salty, and slightly tannic, and tastes of rusty red and orange fruits, peach and apricot pit and skin. It offers greater depth alongside the playfulness expected from a rosé. Because Il Marinetto doesn’t go through malolactic fermentation it’s filtered before bottling.

The first and more upfront of the two Gaglioppo reds, the Cirò Rosso Riserva “Aris” is picked toward the end of September (usually a week or more before “Più Vite,”) and is produced with 40% of its grapes originating from the Piane di Franze vineyard replanted forty years ago at an altitude of 70m and in full view of the sea. Its soil is red clay, red sand, and silt, and the remaining 60% of grapes come from the Piciara vineyard with vines planted seventy years ago on calcareous clay just next to the sea at a few meters in altitude. In the cellar the wine is fermented naturally under a submerged cap with no movements/extractions of the must. After three to four days of fermentation, the wine is drawn from the tank and the grapes are very lightly pressed (with the stronger press juice/wine sold to bulk wine production). Aris is aged in concrete for twenty months prior to bottling, with its first sulfite addition made after malolactic fermentation and then again before bottling. Aris is then aged in bottle for one year before going to market. The total SO2 depends on the vintage and ranges between 30-50 mg/L (ppm). The results are a wine led with beautiful sappy red fruit heavy on cherry nuances with sun-dried red rose, dried sweet orange peel, persimmon, and guava, and loads of iron-led metal/mineral notes. It’s the richer of the two Cirò wines and an easier gateway for newcomers to this historic region.

The Cirò Riserva “Più Vite” is produced only in a few years from the Piciara vineyard on the sea, one with clayey soil and 70-year-old vines. Usually picked in the first week of October, it spends 9-15 days of maceration and spontaneous fermentation under a fully submerged cap without any movements of the must. Like Aris, the wine is then lightly pressed, with the harder pressed wine sold in bulk. As one would expect, this wine has a greater phenolic and tannin ripeness, which leads Sergio to age it for four years in concrete without any movements until bottling. The first sulfite addition is made after malolactic fermentation, with an additional one during the first year of aging (if warranted), and rarely more for the following 2.5 years before bottling. The total SO2 depends on the vintage and ranges between 30-50 mg/L (ppm).
Più Vite’s four years in concrete softens the fruit compared to Aris’ shorter élevage. It’s rustic and savory and young versions often lead with earthy notes of kiln-dried red clay, fall leaves on wet soil, chestnut, saffron, leather, iron, animal, braised meat, and rose water. Fruit is present but delicate, and it emits notes of ripe persimmon, shriveled golden apple, dried orange peel, and wild cherry. More tannic than Aris, Più Vite balances firmness and delicacy. Hours open (even the day after), it rises and can be deceptive, a doppelganger of a top-tier, traditionally made Barolo—tar, plush red rose, sun-touched cherry, and anise. It’s versatile and may be best served with fewer people in an intimate setting with both heart-warming food (ossobuco, cassoulet, ratatouille) and finely crafted, Michelin-style cuisine.




























