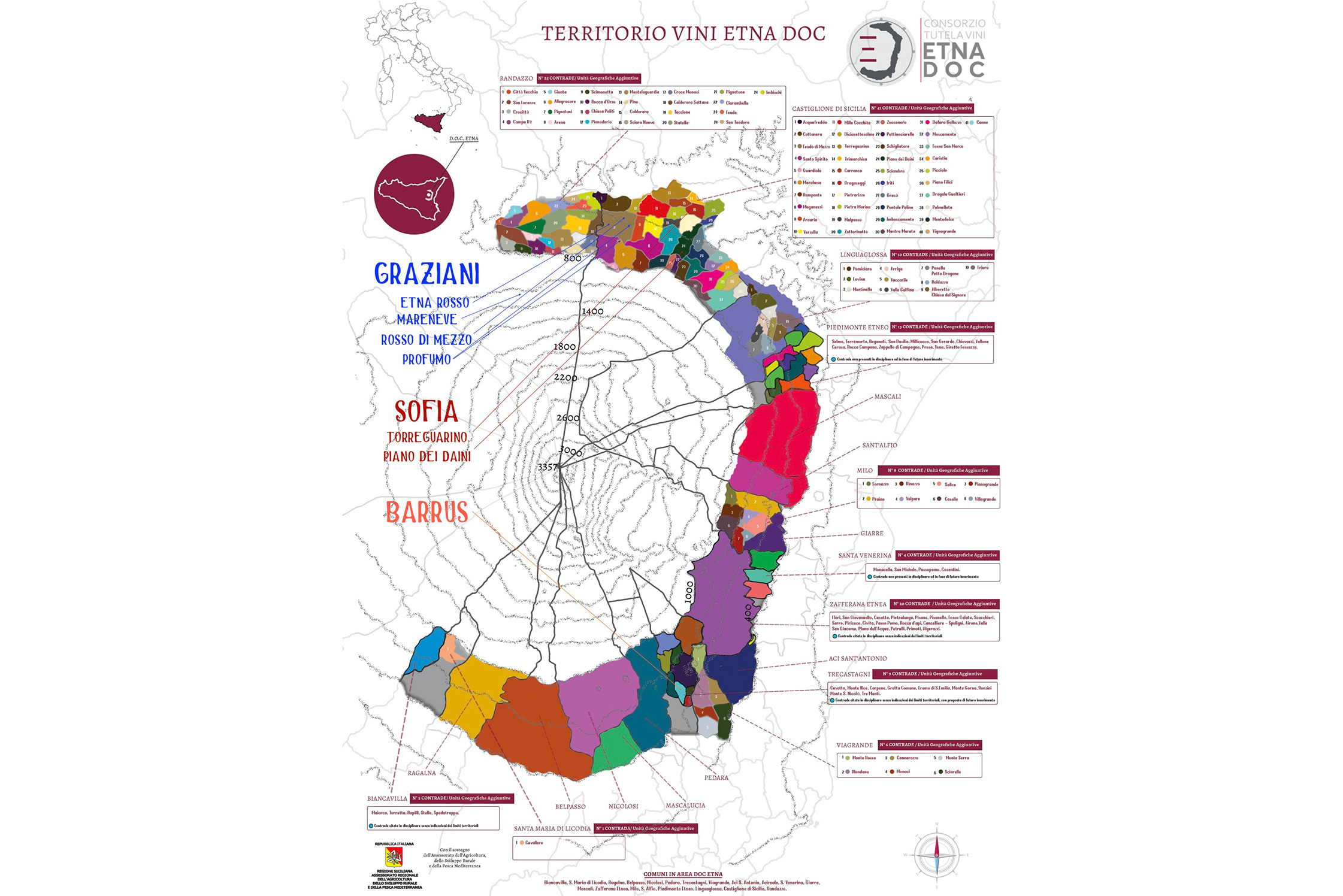
Etna Barrus
This website contains no AI-generated text or images.
All writing and photography are original works by Ted Vance.
Short Summary
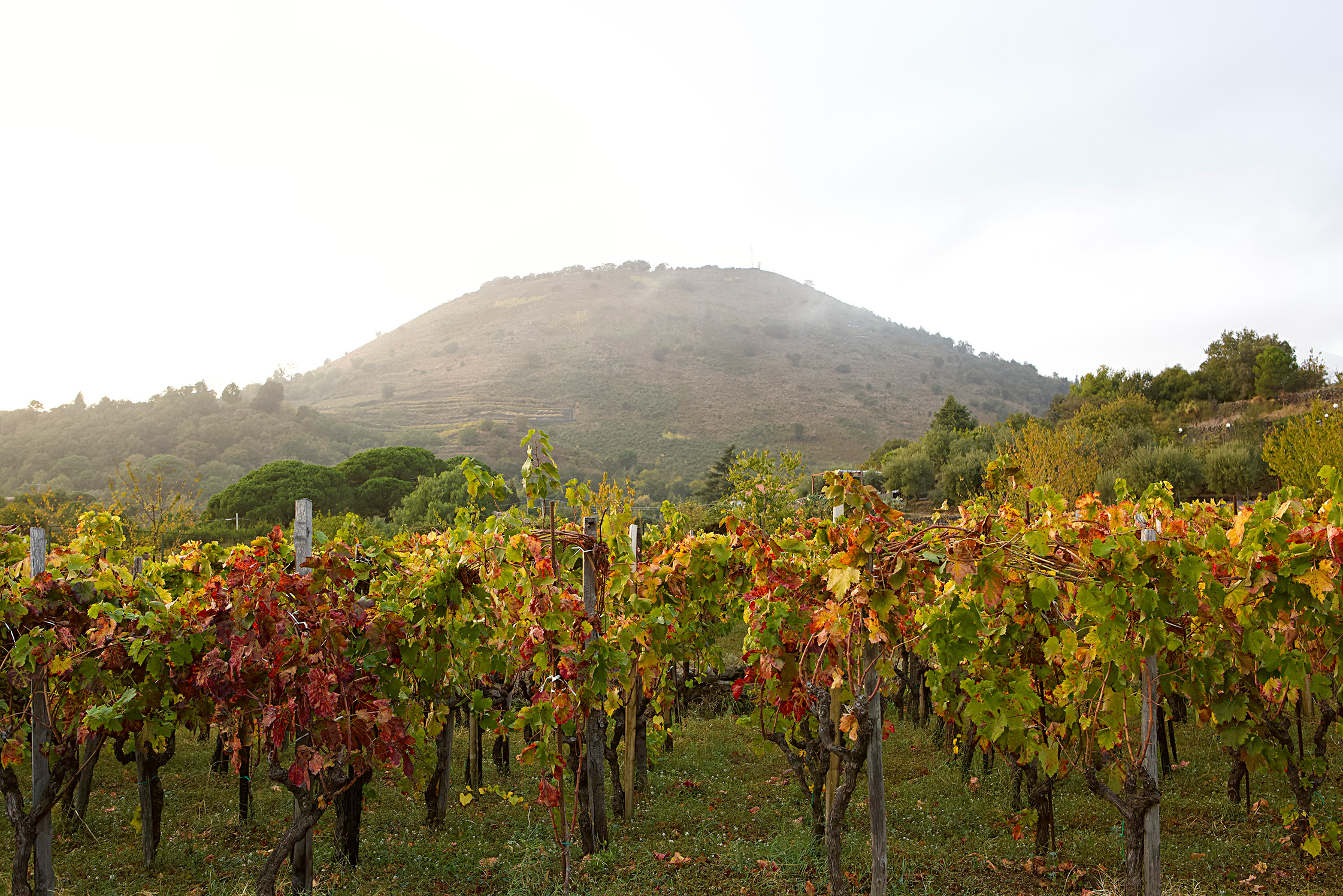
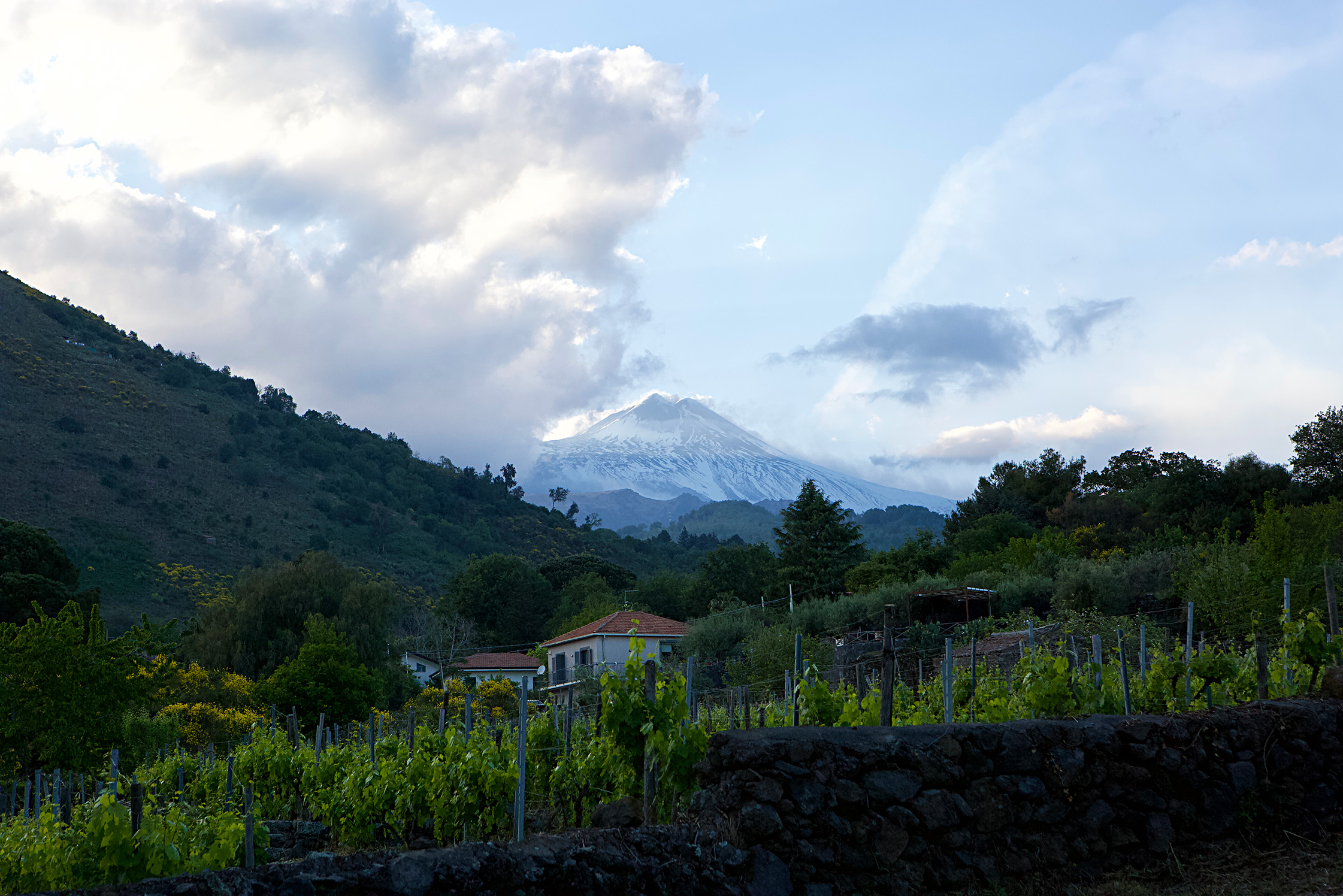
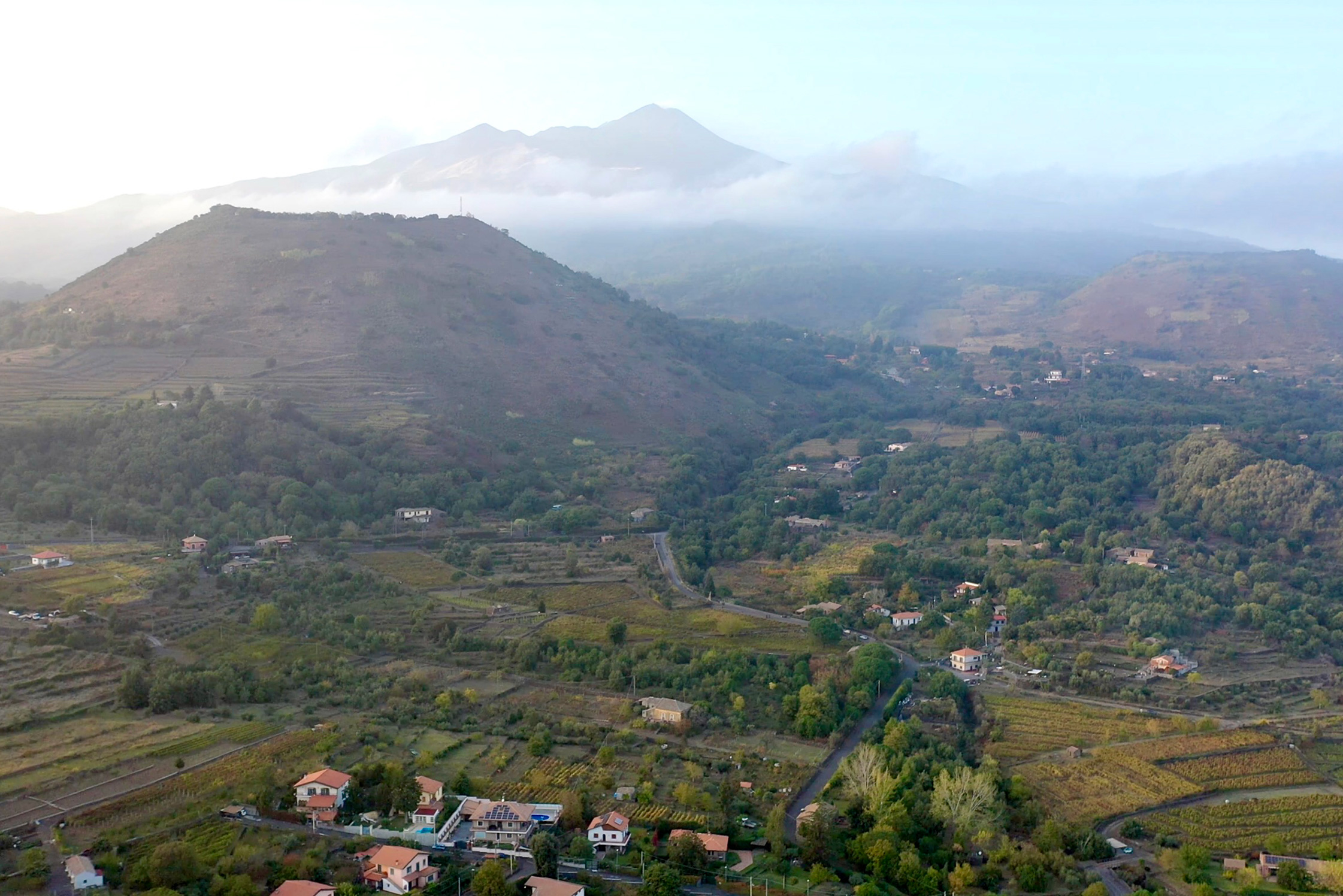
The dream project of three friends, Etna Barrus has 2.7 vineyard hectares planted in 2005 below one of Mount Etna’s extinct cones, Monte Gorna. At 600m altitude with a southeast exposure with an open view of Ionian Sea, their organic massale selections (organic since the beginning, but certification started in 2021) of Nerello Mascalese (90%) and Nerello Cappuccio (10%) grow on sandy volcanic soils rich in organic substances.Full Length Story
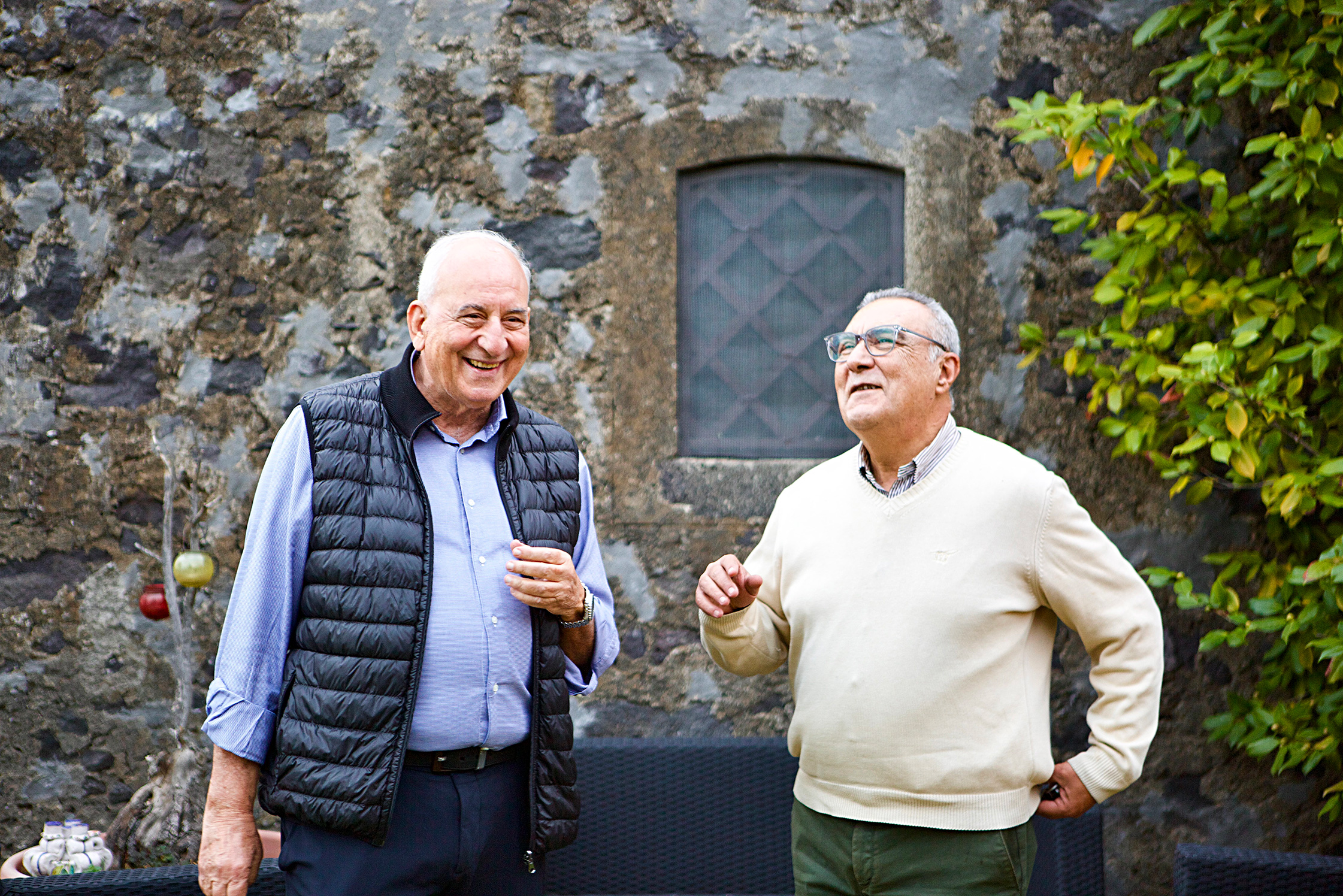
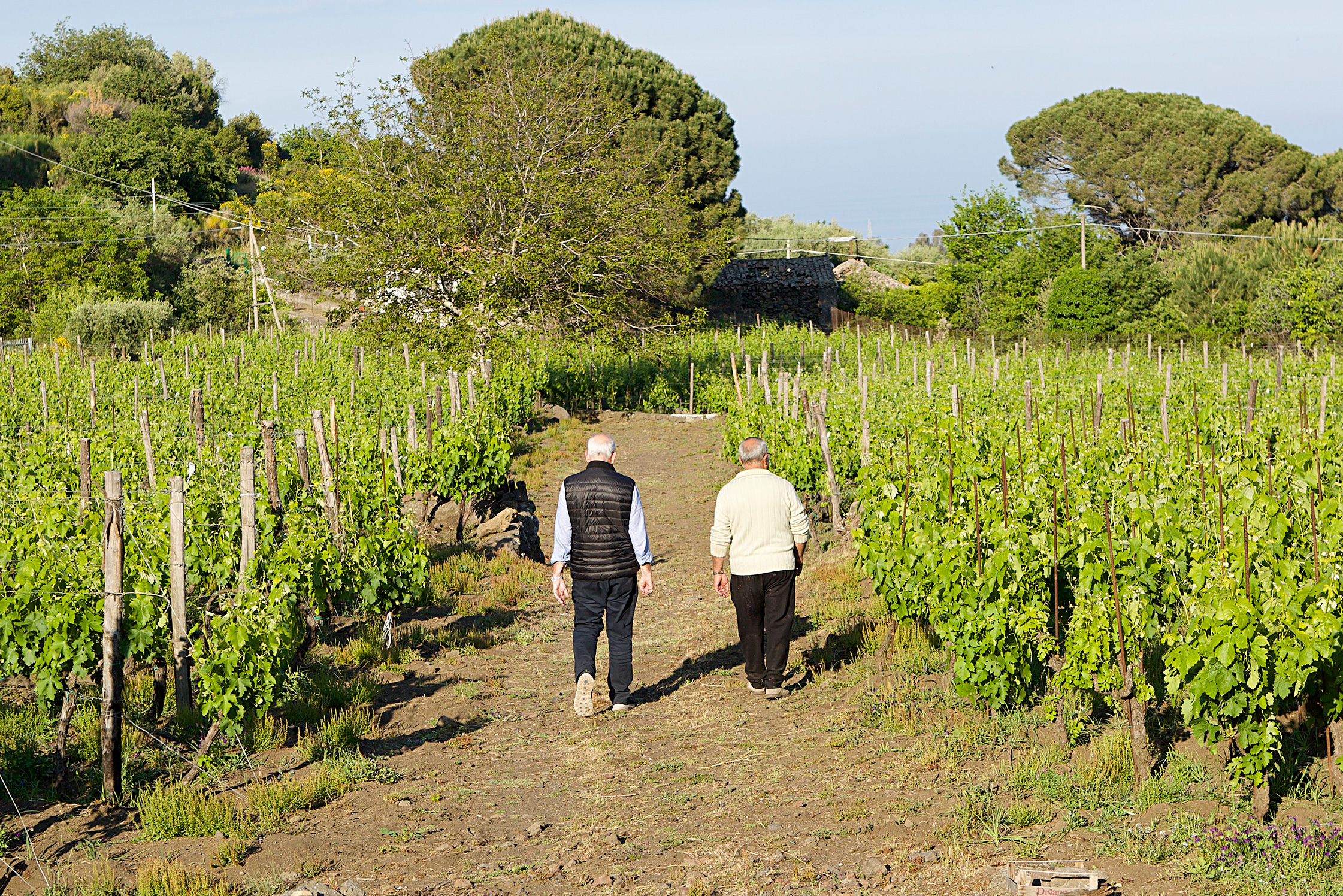
Located at an altitude of six-hundred meters, on panoramic terraces of Mount Etna’s southeast side within view of the Ionian Sea, exists the boyhood dreams of four men. Salvo, Toti, Mario, and Giuseppe were inspired by the passion and work of their grandparents when they formed Etna Barrus, a partnership that would begin their collective return to familial roots, where they would “devote themselves to viticulture without pollution; to do it the way they used to.”
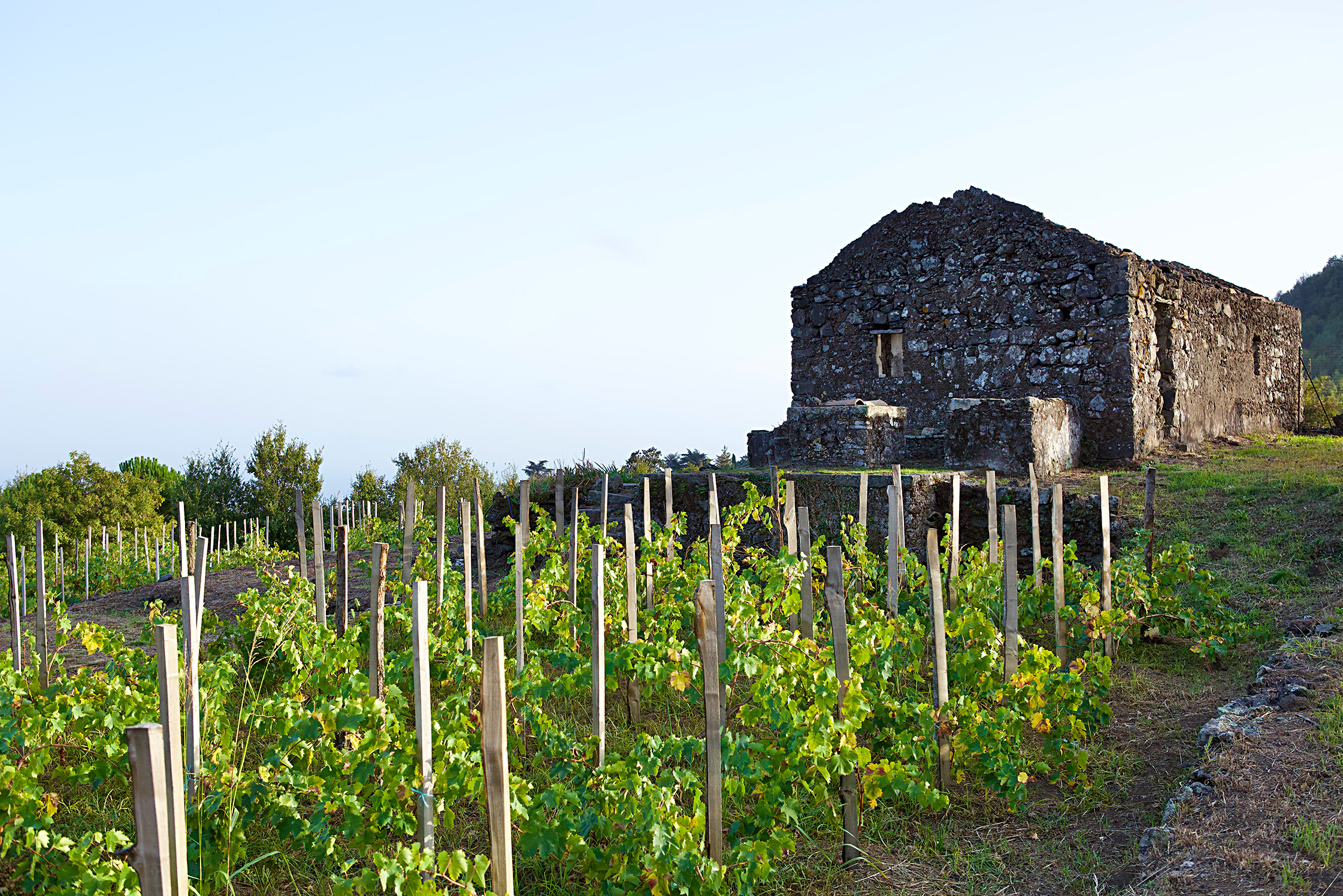
Named after the elephant, the city symbol of Catania, combined with Italy’s most famous active volcano, the vineyards of Etna Barrus were planted in 2005 below one of Etna’s extinct cones, Monte Gorna. Their 2.7 hectares of vines are committed to a red grape responsible for some of the world’s most beguiling wines, Nerello Mascalese, and its burly and more colorful sibling, Nerello Cappuccio; Carricante was also planted in 2021. Their vineyard is composed of massale selections of each variety and they describe their agriculture as regenerative—they’re moving into organic certification in 2023. However, “to do it the way they used to,” implies that even before their bid for organic certification there’ve been no non-organic inputs in their vineyards. And because of the arid conditions in Sicily, with the exposure to the morning sun on the volcano’s southeast face, few treatments are needed in this natural climate that has been favorable to viticulture for millenia.
Their miniscule production churns out two raw though finely nuanced Etna Rosso wines and an Etna Rosato, all a blend of 90% Nerello Mascalese and 10% Nerello Cappuccio, and all on volcanic sand naturally rich in organic substances and life-giving minerals—hallmarks of these nature-friendly soils. The vine density is 5000 vines per hectare trained on Cordone Speronato and Alberello (goblet). The full capacity each season should produce only around 7,500 bottles.
The red grapes are usually harvested around the first ten days of October. Once in the cellar, they are destemmed and macerated no more than a week to preserve the fresher fruit nuances and allow the fine tannins from the grape skins rather than the seeds that further break down as the alcohol rises, extracting harsher tannins. The wine is then racked into steel along with the press wine and then finishes fermentation over another two weeks.
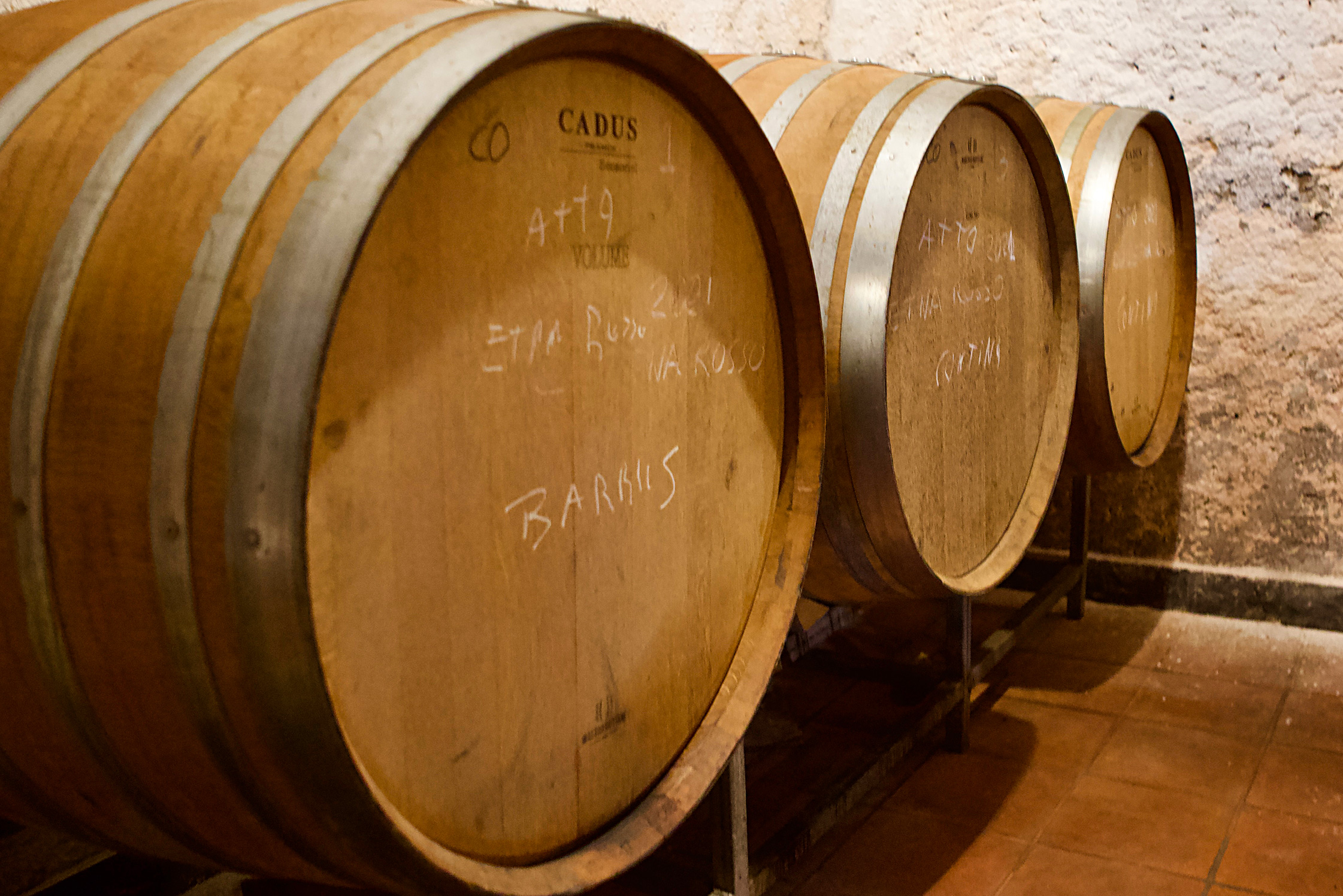
The wine for the purple label remains in steel for a year, and the orange label, the “selezione,” also finishes its fermentation in steel but is then racked into old French oak barrels (225l-500l) for a period of 12 to 18 months, dictated by the season’s conditions. The differences in taste between the Purple Barrus and Orange Barrus Etna Rosso wines are fitting colors that match the wine personalities. Purple Barrus is grown in a more reductive environment (steel) and tends toward a darker color with more exotic purple fruits than red, and has a stronger purple floral element with wild berry fruit. It’s also very mineral in the palate in a refreshingly cool sensation while at the same time being explosive, vigorous and exciting. The orange label Etna Rosso is stronger in red and orange fruits, due to the slow, oxidative maturation in old wood barrels. The floral elements are relatable to the sun-dried rose, similar to Nebbiolo, and expresses the southern Italian sweet orange peel/Aperol aroma. This wine is also more discreet and finely tuned than the upfront purple Barrus.